Designing an innovation management system (IMS) involves creating a structured framework that allows organizations to manage and foster innovation effectively. An IMS encompasses processes, tools, and strategies to generate, evaluate, develop, and implement new ideas. This system aims to create a culture of continuous improvement, creativity, and competitiveness within the organization. Below is a comprehensive guide to designing an innovation management system.
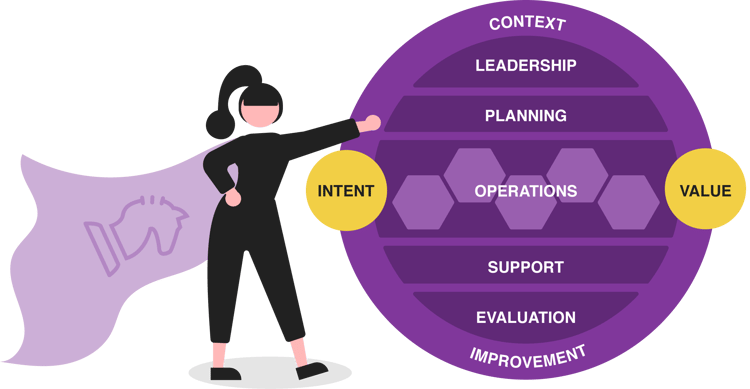
Key Components of an Innovation Management System
Innovation Strategy and Leadership
Idea Generation and Capture
Idea Evaluation and Selection
Development and Implementation
Collaboration and Communication
Measurement and Improvement
Technology and Tools
Culture and Mindset
1. Innovation Strategy and Leadership
An effective IMS begins with a clear innovation strategy aligned with the organization’s overall goals and vision. Leadership plays a critical role in fostering an innovative culture and providing direction.
Vision and Goals: Define a clear vision for innovation, outlining specific goals and objectives that align with the organization’s strategic priorities.
Leadership Commitment: Ensure top management commitment to innovation, demonstrating support through actions and resource allocation.
Innovation Policy: Develop a policy that outlines the organization’s approach to innovation, including guidelines, principles, and roles.
2. Idea Generation and Capture
Creating a systematic process for generating and capturing ideas is essential for fostering innovation.
Sources of Ideas: Encourage ideas from various sources, including employees, customers, partners, and market trends.
Idea Campaigns: Organize idea generation campaigns or challenges focused on specific themes or problems.
Suggestion Systems: Implement suggestion boxes, online portals, or mobile apps where employees can submit ideas anytime.
Brainstorming Sessions: Facilitate regular brainstorming sessions and workshops to stimulate creativity and collaboration.
3. Idea Evaluation and Selection
Not all ideas will be viable; hence, a robust evaluation process is necessary to select the most promising ones.
Evaluation Criteria: Develop clear criteria for evaluating ideas, such as feasibility, impact, alignment with strategy, and potential ROI.
Screening Process: Implement a multi-stage screening process to filter out less promising ideas and focus on high-potential ones.
Cross-Functional Teams: Establish cross-functional evaluation teams to assess ideas from different perspectives and ensure balanced decision-making.
Prioritization Tools: Use prioritization tools like scoring models, matrices, or decision trees to rank ideas based on their potential and strategic fit.
4. Development and Implementation
Once ideas are selected, they need to be developed and implemented effectively.
Project Management: Assign project managers and teams to develop and implement selected ideas, ensuring clear roles and responsibilities.
Agile Methodologies: Use agile methodologies to develop ideas iteratively, allowing for flexibility and continuous feedback.
Prototyping and Testing: Develop prototypes or pilot projects to test ideas in real-world conditions and gather feedback.
Resource Allocation: Ensure adequate resources, including budget, time, and talent, are allocated to innovation projects.
Risk Management: Identify and mitigate potential risks associated with innovation projects through thorough planning and monitoring.
5. Collaboration and Communication
Innovation thrives on collaboration and effective communication.
Collaborative Tools: Implement collaborative tools and platforms that enable team members to share ideas, collaborate on projects, and communicate seamlessly.
Innovation Networks: Create internal and external innovation networks, including partnerships with universities, research institutions, and other organizations.
Knowledge Sharing: Foster a culture of knowledge sharing through regular meetings, workshops, and an accessible knowledge repository.
Open Innovation: Embrace open innovation by involving external stakeholders in the innovation process and leveraging external ideas and technologies.
6. Measurement and Improvement
Regularly measuring and improving the innovation process is crucial for sustained success.
Innovation Metrics: Define and track key performance indicators (KPIs) for innovation, such as the number of ideas generated, projects completed, time-to-market, and ROI.
Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops to gather input from employees, customers, and other stakeholders on the innovation process and outcomes.
Continuous Improvement: Use the feedback and performance data to continuously improve the IMS, making necessary adjustments and refinements.
Recognition and Rewards: Implement recognition and reward systems to incentivize and celebrate successful innovation efforts and contributions.
7. Technology and Tools
Leveraging technology and tools can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the IMS.
Idea Management Software: Use idea management software to capture, track, and evaluate ideas systematically.
Collaboration Platforms: Implement platforms like Microsoft Teams, Slack, or Confluence to facilitate communication and collaboration.
Project Management Tools: Utilize project management tools like Trello, Asana, or Jira to manage innovation projects and track progress.
Data Analytics: Employ data analytics to analyze trends, measure performance, and make informed decisions.
8. Culture and Mindset
A supportive culture and mindset are essential for fostering innovation.
Encourage Experimentation: Promote a culture that encourages experimentation and tolerates failure as a learning opportunity.
Empower Employees: Empower employees to take initiative, share ideas, and participate actively in the innovation process.
Leadership by Example: Leaders should model innovative behavior and demonstrate a willingness to take risks and embrace change.
Training and Development: Provide training and development opportunities to build innovation skills and capabilities within the organization.
Conclusion
Designing an effective innovation management system involves creating a structured framework that fosters creativity, collaboration, and continuous improvement. By aligning innovation with strategic goals, implementing robust processes, leveraging technology, and nurturing a supportive culture, organizations can enhance their ability to innovate and maintain a competitive edge. Continuous measurement and improvement ensure the IMS evolves with changing needs and challenges, driving sustained success in the dynamic business environment.